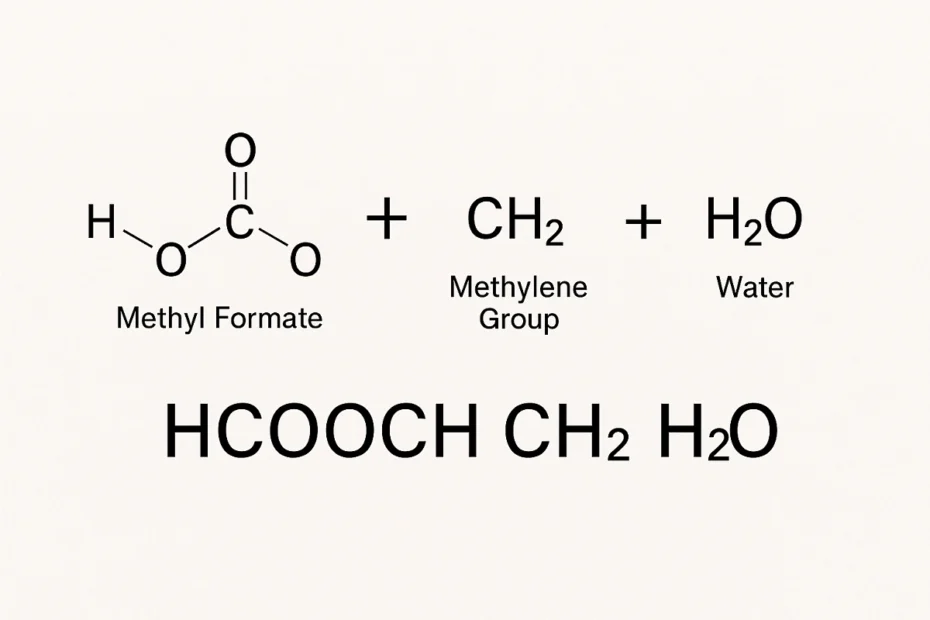
In the world of chemistry, understanding how compounds interact is key to unlocking new technologies and solving everyday problems. One such chemical interaction that has sparked interest in both academic and industrial settings is HCOOCH CH2 H2O. While this combination may look complex, it has interesting applications and reactions that are crucial in organic chemistry and chemical synthesis.
In this article, we will dive deep into what HCOOCH CH2 H2O means, how these compounds interact, their chemical properties, reactions, and real-world uses. If you’re a student, researcher, or enthusiast trying to understand this combination, this guide is tailored for you.
What Does HCOOCH CH2 H2O Represent?
Let’s break it down:
-
HCOOCH: This is commonly the molecular formula for methyl formate, an ester derived from formic acid and methanol.
-
CH2: This generally refers to a methylene group, which is a part of many organic molecules.
-
H2O: This is water, a universal solvent and participant in many chemical reactions.
So, when we refer to HCOOCH CH2 H2O, we are likely discussing a reaction that involves methyl formate, a methylene compound (possibly formaldehyde or methylene chloride), and water.
Possible Reactions Involving HCOOCH CH2 H2O
When these compounds are combined, one of the most probable interpretations is a hydrolysis reaction or an organic synthesis involving methyl formate, a methylene-based compound, and water.
1. Hydrolysis of Methyl Formate
Methyl formate (HCOOCH₃) can undergo hydrolysis in the presence of water:
HCOOCH₃ + H₂O → HCOOH + CH₃OH
This reaction breaks the ester bond and produces:
-
Formic acid (HCOOH)
-
Methanol (CH₃OH)
This is an important industrial reaction, especially in the production of formic acid.
Now, if CH₂ is involved as part of another compound (like formaldehyde CH₂O), additional steps could occur, potentially leading to polymerization or further breakdown.
Significance of Each Component
HCOOCH – Methyl Formate
Methyl formate is a colorless liquid with a pleasant odor, widely used as a solvent and in manufacturing:
-
Pharmaceuticals
-
Perfumes
-
Agricultural chemicals
It is also important in producing formic acid through hydrolysis.
CH2 – Methylene Group
The methylene group (–CH₂–) is a key part of organic chemistry. It acts as a bridge in hydrocarbon chains and is reactive in:
-
Aldehyde formation (e.g., formaldehyde – CH₂O)
-
Chlorinated solvents (e.g., methylene chloride – CH₂Cl₂)
H2O – Water
Water is a universal participant in chemical reactions. It’s the main solvent in biochemical processes and often involved in:
-
Hydrolysis
-
Condensation
-
Acid-base reactions
Industrial Applications of HCOOCH CH2 H2O Reactions
The interaction between HCOOCH, CH2, and H2O is more than just a lab experiment. These reactions have real-world implications.
1. Formic Acid Production
As mentioned earlier, hydrolyzing methyl formate yields formic acid, widely used in:
-
Leather production
-
Textile dyeing
-
Preserving animal feed
2. Solvent Recovery and Recycling
Methyl formate and methylene chloride (if used) are volatile solvents. Combining and processing them in water-based systems can allow for solvent recovery, reducing environmental impact.
3. Polymer Industry
If the CH2 component is part of formaldehyde, the resulting reactions can lead to polymer precursors, like polyoxymethylene, used in:
-
Automotive parts
-
Electrical components
-
Precision gears
Laboratory and Environmental Considerations
When handling HCOOCH CH2 H2O, safety and environmental precautions are essential.
Laboratory Handling
-
Use fume hoods when working with volatile compounds like methyl formate and methylene chloride.
-
Ensure proper PPE: gloves, goggles, and lab coats.
-
Use sealed containers to avoid vapor exposure.
Environmental Impact
-
Methyl formate is considered less harmful than many other esters but must still be disposed of properly.
-
Water-based reactions are often preferred to reduce toxic solvent use.
-
CH2 compounds like methylene chloride are toxic and potentially carcinogenic—use substitutes when possible.
How This Reaction Connects to Green Chemistry
Green chemistry focuses on designing products and processes that reduce hazardous substances. The reaction involving HCOOCH CH2 H2O fits into green chemistry in a few ways:
-
Use of water as a solvent reduces reliance on organic solvents.
-
Hydrolysis reactions are often milder and less toxic.
-
By optimizing the process, industries can create biodegradable and less harmful by-products.
Educational Importance
Understanding the chemistry behind HCOOCH CH2 H2O provides foundational knowledge in:
-
Organic synthesis
-
Ester hydrolysis
-
Functional group reactivity
This makes it a common topic in chemistry textbooks, university labs, and entrance exams for higher studies.
Summary: Why HCOOCH CH2 H2O Matters
The interaction of HCOOCH CH2 H2O may seem complex at first glance, but its implications are far-reaching. From formic acid production to polymer synthesis, and even green chemistry, this combination plays a valuable role in modern chemistry.
To recap:
-
HCOOCH CH2 H2O can lead to hydrolysis and synthesis reactions.
-
The key products often include formic acid, methanol, and potentially polymer precursors.
-
These reactions are relevant in both industrial and academic settings.
-
Environmental and safety protocols must be observed due to potential toxicity.
If you are studying organic chemistry or working in chemical industries, understanding this combination is not just useful—it’s essential.